Menu bar
| File | ||
| Open Image | Alt-I | Load an image or volume |
| Open DICOM | Alt-D | Load a DICOM folder. Make sure it is the folder containing the .dcm files! If the folder contains more studies you will be asked to select one. |
| Open Mask | Alt-M | Load a mask |
| Open DICOM as Mask | Alt-N | Load a DICOM folder as a mask |
| Open Mesh | Alt-E | Load a mesh file |
| Save Image | Ctrl-I | Save the current image or volume |
| Save Image as DICOM | Ctrl-D | Save the current image or volume as a DICOM in a folder |
| Save Mask | Ctrl-M | Save the mask |
| Save Mask as Contours | Ctrl-J | Save the mask as RT Struct or GeoJSON by generating contours in the x-y plane |
| Save Mask as DICOM | Ctrl-N | Save the mask as a DICOM in a folder |
| Save Mesh | Ctrl-E | Save the mesh |
| Export Time Series | Ctrl-T | Save the mesh |
| Export Time Series Mask | Ctrl-Y | Save the mesh |
| Edit | ||
| Setting | Alt-S | Open the settings menu |
| Undo | Ctrl-Z | Undo the last operation. You can apply undo only 10 times. |
| Clear | Remove the image/volume, mask and shape data | |
| View | ||
| Process Panel | Show/hide the Process panel | |
| Segment Panel | Show/hide the Segment panel | |
| View Panel | Show/hide the View panel | |
| Info Panel | Show/hide the Info panel | |
| Output Panel | Show/hide the Output panel. The Output panel at the bottom displays real-time information about the operations of ScanXm. | |
| Full Screen... | F11 | Maximize the window |
| Help | ||
| About... | Ctrl-F1 | Show ScanXm information including the Device ID |
| Controls | Open a window which details all the mouse and keyboard controls | |
| Acknowledgements | Open a window which shows all the acknowledgements |
Right panel
On the right we have a standard four panel view for the volume. It shows the plane for each axis. With the scroll bar you can scroll through the slices. Change the brightness by dragging the mouse with the right button pressed from left to right. Change the contrast by dragging the mouse up and down. This is similar to changing the level and window. With the mouse wheel you can zoom in and out. Holding the middle mouse button allows you to drag the image around.In the top left window we can select what to show using checkboxes with text. These includes from left to right:
|
crosshair
|
A crosshair to indicate the location of the planes.
|
|
mask
|
The mask in case this is available.
|
|
shape
|
The shape in case this is available.
|
On the right side we find picture buttons with the following functions:

This play button scrolls through the slices
The movie camera allows you to make a movie

The photo camera allows you to make a screenshot
Fits the image to the screen
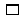
With this button the window this button belongs to will span accros all 4 windows, and the other windows will disapear.
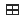
This button will resore the view to all four windows.
The bottom right gives us the 3D view. This view again has a top bar with on the left the following checkboxes:
|
outline
|
Show the box
|
|
planes
|
Show the three planes
|
|
shape
|
Show the surface mesh
|
|
volume
|
Show the volume rendering
|
On the right you can again see some picture buttons with the following functions:
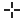
Select the location of the slices or set the camera focal point on mesh when using depth of field
rotate the volume

Rotate the volume
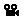
Movie camera you can then make a movie

The photo camera allows you to make a screenshot

Generate an oblique View perpendicular to view direction, pressing again will fix this view

Toggle various preset views

Fits the image to the screen

With this button the window this button belongs to will span accros all 4 windows, and the other windows will disapear.

This button will resore the view to all four windows.
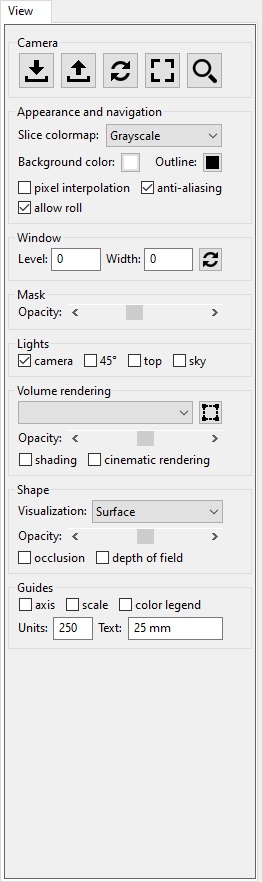
View panel
The panel on the left has an upper and lower part. Both parts have tabs that provide an interface for the functions of ScanXm. The top panel has a "Process" and "Segment" panel. The bottom panel has a "Info" and "View" panel. The "Info" gives an overview of the image and surface properties when available. In the "View" panel you can change many of the visual properties in ScanXm. They are defined in boxes.Camera

Store camera position for all view panels

Restore camera position for all view panels

Restore camera positions in each view to default

In each view the volume/image is fitted into the viewing area

Toggle button when selected you can zoom in/out
Appearance and navigation
|
|
Select the colormap used in the slices of a scalar volume. |
|
Background color:
|
Select the backgound color |
|
Outline:
|
Select the color of the box outline |
|
bilinear interpolation
|
Use a bilinear interpolation to make the images appear smooth instead of seeing the individual pixels/voxels. |
|
allow roll
|
If not checked the volume in the bottom right view will remain upright. |
Window
|
|
The window level defining the centre point of the intensity range. |
|
|
The window width defining the range of grey scale values. |
|
Reset the window level and width to encompass the entire range of intensity values. |
Mask
|
Opacity:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
Adjust the transparency of the mask. |
Lights
|
camera
|
The light originates from the camera position. |
|
45°
|
The light is at a 45 degree angle from the top. |
|
top
|
The light is pointing down from the camera view. |
|
sky
|
The light is shining down in the z-direction as if from the sky. |
Volume rendering
|
|
Select a preset transfer function. |
|
Show the bounding box to constrain the volume rendering. |
|
Opacity:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
Set the transparency of the volume rendering. |
|
shading
|
Add shading in the volume rendering. |
|
cinematic rendering
|
Perform cinematic rendering. |
Shape
|
|
Set the type of visualization for the mesh. |
|
Opacity:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
Set the transparency when transparent mesh rendering is selected. |
|
occlusion
|
Add ambient occlusion to the mesh rendering. |
|
depth of field
|
Add depth of field to the mesh rendering. |
Guides
|
axis
|
Show the x, y and z-axis direction. |
|
scale
|
Add a scale bar. |
|
color legend
|
Add a color legend. |
|
|
Set the units for the scale bar. |
|
|
Set the text that is displayed with the scalebar. |
Process panel
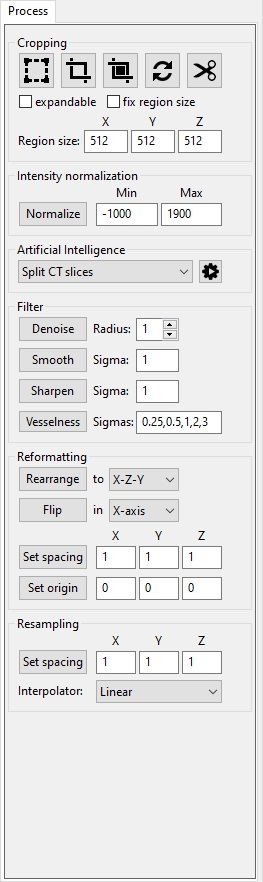
The "Process" panel provides various tools to modify the image. This includes tools to set the image properties, crop or resample the image, and various filters.Cropping

Show the box region of interest.

Fit the box to the tissue.

Fit the box to the mask.

Reset the box to the total volume region.

Crop the volume to the box region.
|
expandable
|
Allow the box to expand beyond the region of the volume.
|
|
fix region size
|
Fix the size of the box to the values below.
|
|
Region size:
|
The size in the x, y and z-direction of the box when fix region size is checked. |
Intensity normalization
|
|
Normalize the volume to have the given minimum and maximum value. |
Artificial Intelligence
|
|
Select one of the AI processing functions. |
|
Run the selected AI processing fuction. |
Filter
|
|
Denoise the volume using a kernel with the given radius. |
|
|
Smooth the volume using a gaussian with the given sigma. |
|
|
Sharpen the volume using a gaussian with the given sigma. |
|
|
Enhance vessel structures. The comma seperated sigmas represent the resolutions onto which the filter is applied, which are merged for a final result. |
Formatting
|
|
Change the axis according to the X, Y and Z order selected in the dropdown list. |
|
|
Flip the image or volume in the selected axis. |
|
|
Set the pixel/voxel spacing. |
|
|
Set the origon for the image or volume. |
Resampling
|
|
Set the pixel/voxel spacing. |
|
|
Set the interpolator for when resampling the image/volume. |
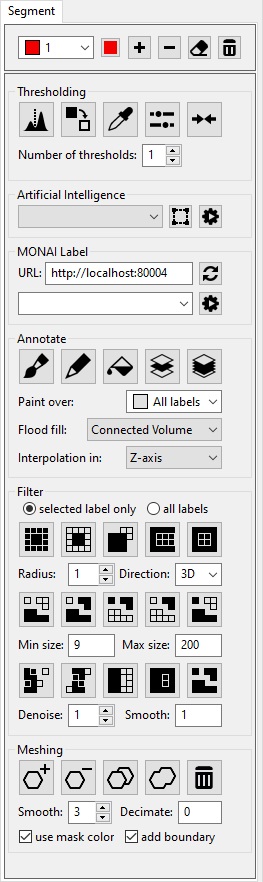
Segment panel
The "Segment" panel has all the function to be able to generate a segmentation of the structures in the image. This includes automatic segmentations, but also tools to manually annotate the images. It also has a wide range of filters to further process the label map. Finally, it also includes fuctions to generate a surface mesh from the label maps.Thresholding

Find the thresholds automatically using the Otsu method. Select the number of labels to find the threshold for below.

Change the label to the selected label by clicking on the other label in the slice view.

Select a set of pixels by drawing a region. The greyscale or color values of these pixels wil be used to update the threshold of values of the selected label.

Pressing this button will open a window with scrollbars to manually adjust the threshold values.

This will move the thresholds of multiple labels together.
|
|
The number of labels to find the threshold for. |
Artificial Intelligence
|
|
Select the organ to segment automatically. |
|
Show the bounding box to constrain the AI segmention. Moving the box to only the region of interest will make the automatic segmentation faster. |
|
Run the AI based automatic segmentation. |
MONAI Label
|
|
Enter the URL of the MONAI server. |
|
Reset the MONAI server information. This operation will add the available models to the dropdown box below. |
|
|
This will contain all the available models when the refresh button is pressed. Select the model you wish to run here. |
|
Run the selected MONAI model. |
Annotate

Use the paintbrush to draw label values on the mask.

Use the pen delineation tool to draw regions in the image to fill with the label value.

The flood fill tool will fill an entire label region with the selected label value. How the region is defined can be selected in the Flood fill dropdown box below.
Interpolate the selected label in the selected empty plane based on the distance field. The "Interpolation in" dropdown menu below determines the plane in the associated axis.
Interpolate the label map in all empty slices that lay between two non empty slices in the axis defined by the "Interpolation in" dowpdown box.
|
overwrite other labels
|
If this is checked, drawing or delineating will always overwrite the pixel with the new label. |
|
|
Select which label values are overwritten. |
|
|
Select how the region is defined in a flood fill operation. Connected Slice: Apply to connected region in the slice. Connected Volume: Apply to connected region in the volume. Connected Temporal: Apply to temporally connected region. All in Slice: Apply to all regions in the slice. All in Volume: Apply to all regions in the volume. All in Temporal: Apply to all the regions in all time points. |
|
|
This defined in which plane the label is interpolated. The X-Y plane is shown in the bottom-left panel, the X-Z plane is the top-left panel and the Y-Z the top-right panel. |
Morphological operators
|
|
Perform below operations only on the selected label or all labels. |

Apply a dilation operation with the below radius on the mask of the selected label.

Apply a erosion operation with the below radius on the mask of the selected label.

Apply a opening operation with the below radius on the mask of the selected label.

Apply a closing operation with the below radius on the mask of the selected label.

Fill all holes in the mask of the selected label.
|
|
The radius of the kernel used in the morphological operation. |
|
|
This defined in which direction the morpological operation is performed. If "3D" is selected it is performed volumetrically. Otherwise it is applied in the repective plane. |

Keep only the largest region.

Remove the regions smaller than the minimum size defined below.

Remove the regions larger than the maximum size defined below.

Remove the regions smaller than the minimum size and larger than the maximum size defined below.

Keep only the regions smaller than the minimum size and larger than the maximum size defined below.
|
|
The minimum size used in the above region based operations. |
|
|
The maximum size used in the above region based operations. |

Denoise the mask using a majority filter with a radius defined below.

Smooth the mask using a gaussian filter with a sigma defined below.

Perform opening operations with increasing diameter until there are no more handles.

Perform closing operations with increasing diameter until there are no more handles.

Relabel the smaller connected regions of each label to form a segmentation with only one connected region for each label.
|
|
Denoising kernel radius. |
|
|
Ammount of smoothing. |
Meshing
Add a surface mesh for the selected label.
Remove the surface mesh for the selected label.

Add a surface mesh of every label.

Generate a surface mesh of all the labels merged together. If the "use mask color" checkbox is checked, each point on the surface mesh will be assigned the correct color, which will blend smoothly between them on the surface triangles.

Remove all the meshes.
|
|
The number of surface smoothing iterations. |
|
|
Decimate the mesh between 0 (none) and 1 (fully). |
|
use mask color
|
Assign a color to the mesh based on the label color. |
|
add boundary
|
Close the mesh at the boundary of the volume. |